How to Implement Data Deduplication using PowerShell
In this post, I want to show you how to install and configure the role of Data Deduplication in Windows Server 2016 using Windows PowerShell. Data Deduplication is a role service that conserves storage space on an NTFS volume by locating redundant data and storing one only copy of that data instead of multiple copies.
Requirements #
- System or boot volumes are not supported
- Volumes must be using NTFS or ReFS
- Volumes must be attached to the server and cannot appear as non-removable drives
- Volume can be shared storage
- Certain files will not be processed
- Files with extended attributes
- Encrypted files
- Files smaller than 32 KB
Usage Types #
- General purpose file servers.
- General file shares.
- Virtualized Desktop Infrastructure.
- Virtual hard disks
- Virtualized Backup Applications.
- Backup volumes
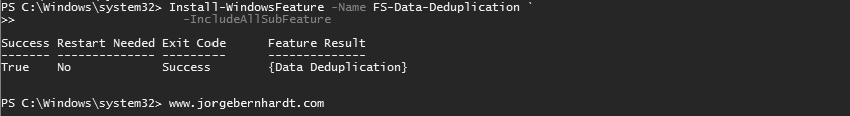
Install Data Deduplication by using Windows PowerShell #
You can do this using the Install-WindowsFeature cmdlet with the following syntax:
Install-WindowsFeature `
-Name FS-Data-Deduplication `
-IncludeAllSubFeature
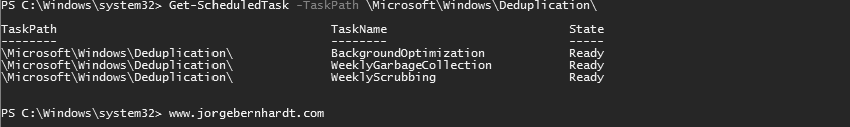
Get-ScheduledTask `
-TaskPath \Microsoft\Windows\Deduplication\
- BackgroundOptimization: The Optimization jobs deduplicate data and compress file chunks on a volume per the policy settings.
- WeeklyGarbageCollection: The Garbage Collection job reclaims disk space by removing unnecessary chunks that are no longer being referenced.
- WeeklyScrubbing: The Integrity Scrubbing job identifies corruption in the chunk store due to disk failures or bad sectors.
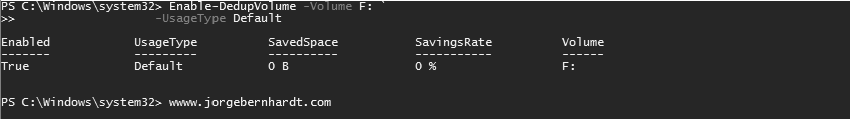
Enable Data Deduplication on a volume #
To enable deduplication on a volume, run the Enable-DedupVolume with the following syntax:
Enable-DedupVolume `
-Volume <String[]> `
-UsageType <UsageType>
Set the data deduplication settings on the volume #
If you want to set additional settings on a volume, use the Set-DedupVolume cmdlet with the following syntax:
Set-DedupVolume `
-Volume <String[]> `
-OptimizeInUseFiles `
-NoCompress <Boolean> `
-NoCompressionFileType <String[]> `
-MinimumFileAgeDays <UInt32> `
-MinimumFileSize <UInt32> `
-ExcludeFolder <String[]> `
-ExcludeFileType <String[]>
- -OptimizeInUseFiles: Indicates the behavior of the server when optimizing the files in use.
- -NoCompress: Indicates whether or not the server compresses data after deduplication.
- -MinimumFileAgeDays: The deduplication process optimizes the files that users have not accessed in the number of days that you specify in this parameter.
- -MinimumFileSize: Specifies the minimum size in bytes.
- -ExcludeFileType: Specifies comma-separated values of the extension types that are excluded by the deduplication engine.
- -ExcludeFolder: Specifies an array of folders in which all files are ignored during data deduplication.
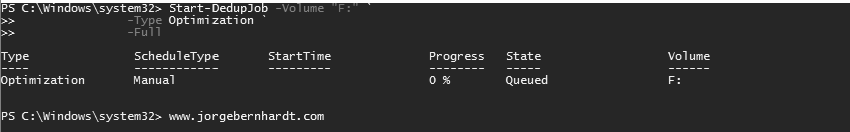
Run data deduplication jobs on demand #
By default, deduplication occurs in the background, as a low-priority process, when the system is not busy but if you want to execute these jobs manually. Use the Start-DedupJob cmdlet with the following syntax:
Start-DedupJob `
-Volume <String[]> `
-Type <Type> `
-Memory <UInt32> `
-Cores <UInt32> `
-Priority <Priority> `
-StopWhenSystemBusy `
-Preempt `
-Full `
-ReadOnly
- -Type: Specifies the type of data deduplication job.
- -Memory: Specifies the maximum percentage of physical computer memory that a job can use.
- -Cores: Specifies the maximum percentage of physical cores that a job uses.
- -Preempt: Indicates that the deduplication engine moves the job to the top of the job queue and cancels the current job.
- _-ReadOnly:_ Indicates that the scrubbing job only reports the damage it finds but does not perform any repair action.
Monitor Deduplication #
Once you have installed data deduplication and enabled it on volumes. You can monitor the deduplication process using the Get-DedupStatus cmdlet with the following syntax:
Get-DedupStatus `
| format-list
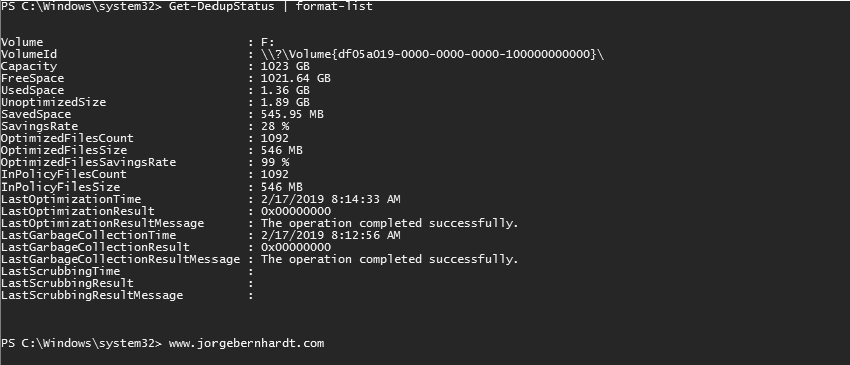
You can also review the history of a server’s deduplication jobs on the Windows event logs. Data Deduplication events are located in the application and Services Logs\Windows\Deduplication\Operational container.
Thanks for reading my post. I hope you find it useful.
If you want to know more about Data Deduplication, check out this link.